Efficient Communication in MARL via Variance Based Control
이 논문을 읽게 된 이유: Communication 최근 논문 서칭 중 발견한 논문. 제목으로 봐서는 channel을 직접적으로 모델링 하는게 아니라 Message로 이슈를 넘기는 듯한 기분이 들었음. NIPS 2019 PDF
Introduction
-
Three lines of research that try to mitigate the instability and indfficiency caused by decentralized execution
-
Independent Q-learning : Does not account for instability casued by environment dynamics
-
Centralized training and decentralized execution
-
Communication among agents during execution : Overhead in terms of latency and bandwidth
- its success is heavily dependent on the usefulness of the received information.
-
- Problem
- Often superfluous(unnecessary) for an agent to wait for feedback from all surrounding agents before making an action decision. i.e. the front camera trigger ‘brake’ signal without waiting for the feedback from the other parts of the vehicle
- The feedback received from the other agents may not always provide useful information. i.e. the navigator should pay more attention to the messages sent by the perception system rather than by the entertainment parts.
- Excessive amount of communication may introduce useless and even harmful information which could even impari the convergence of learning.
- This paper
- Fully cooperative senario
- Centralized learning and decentralized execution + Communication
- Inserting an extra loss term on the variance of the exchanged information, the valuable and informative part inside the messages can be effectively extracted and leveraged to benefit the training of each individual agent.
- Initiates communication only when its confidence level on this preliminary decision is low.
- the agent replies to the request only when its message is informative.
Methods
- The main idea of VBC is to achieve the superior performance and communication efficiency by limiting the variance of the transferred messages.
- During execution, each agent communicates with other agents ony when its local decision is ambiguous.
- The degree of ambiguity is measured by the difference on top two largest action values.
- The agent replies only if its feedback is informative, namely the variance of the feedback is high.
Network
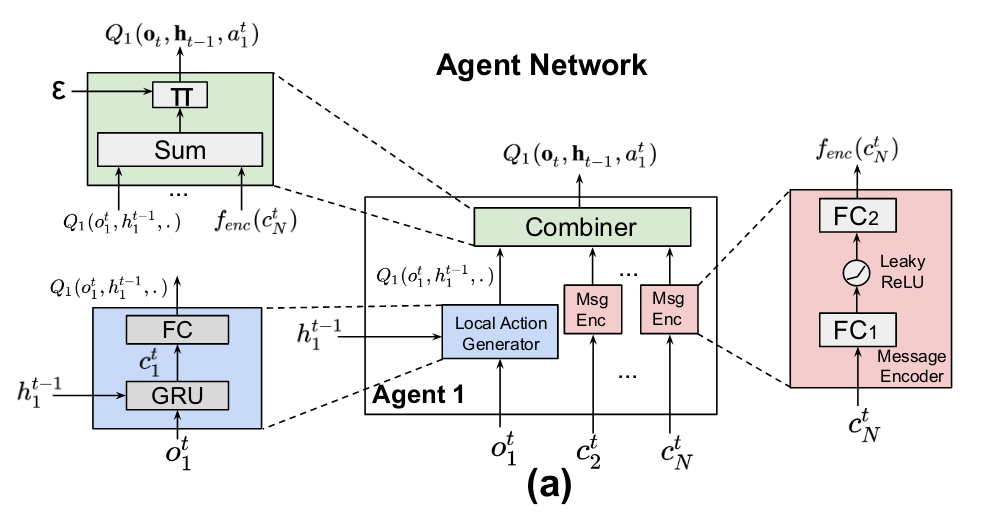
-
Local Action Generator
- GRU + FC
- Inputs : \(o^{t}_{i}, h^{t-1}_{i}\)
- Output : \(Q_{i}(o^{t}_{i}, h^{t-1}_{i}, a^{t}_{i})\) for each action \(a^{t}_{i} \in A\)
-
Message Encoder
- MLP(2 \(\times\) FC)
- Multiple independent message encoders
- Inputs : each accepts \(c^{t}_{j}, j \neq i\) from another agent
- Output : \(f^{ij}_{enc}(c^{t}_{j})\) w/the same dimension as that of local action generator
-
Combiner
-
Inputs : the outputs from both local action generator \(Q_{i}(o^{t}_{i}, h^{t-1}_{i}, \cdot)\) and message encoders \(f^{ij}_{\text{enc}}(c^{t}_{j})\) where \(j \neq i\)
-
Output : produces the global action-value function \(Q_{i}(o_{t}, h_{t-1}, a^{t}_{i})\) of agent \(i\)
-
Do not introduce extra parameters fo combiner
\[Q_{i}(o_{t}, h_{t-1}, \cdot) =Q_{i}(o^{t}_{i}, h^{t-1}_{i}, \cdot) + \sum_{j \neq i}f^{ij}_ {\text{enc}}(c^{t}_{j})\] -
Chooses the action with the \(\eps\)-greedy policy, \(\pi(\cdot)\).
-
-
To preventthe lazy agent problem and decrease the model complexity, maek \(\theta^{ij}_{enc}\) is the same for all \(i\) and \(j(j \neq i)\), and also make \(\theta ^{i}_{local}\) the same for all \(i\).
Loss Fuction
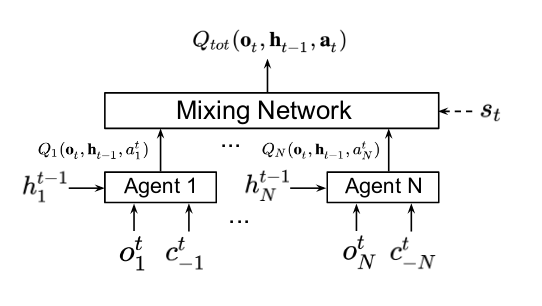
-
Employ a mixing network to aggregate the action-value funtion \(Q_{i}(o^{t}_{i}, h^{t-1}_{i}, a^{t}_{i})\) to yield \(Q_{tot}(o_{t}, h_{t-1}, a_{t})\)
-
To limit the variance of the messages from the other agents, introduce an extra loss term on the variance of the outputs of the message encdoers \(f_{enc}(c^{t}_j)\).
\[\mathcal{L}(\theta_{local}, \theta_{enc}) = \sum_{b=1}^{B} \sum_{t=1}^{T} \big[ (y^{b}_{tot} - Q_{tot}(o^{b}_{t}, h^{b}_{t-1}, a^{b}_{t}; \theta))^{2} + \lambda \sum_{i=1}^{N} Var(f_{enc}(c^{t,b}_{i})) \big]\]
Communication Protocol Design
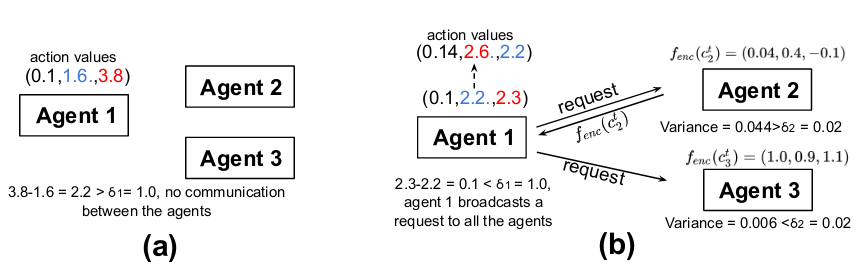
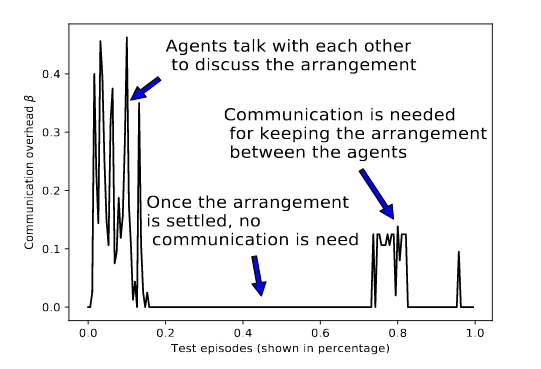
- Each agent only consults with the other agents when its confidence level on the local decision is low, and the other agents only reply when their messages can potentially change the final decision.
- Agent \(i\) first computes the local action-value function \(Q_{i}(o^{t}_{i}, h^{t-1}_{i}, \cdot)\) and \(f^{ij}_{\text{enc}}(c^{t}_{j})\).
- Measure the fonfidence level on the local decision by computing the difference between the largets and the second largest element within the action values.
- Upon receiving sthe request, only the agents whose message ahs a large variance reply, since their messages may change the current action decisiona agent 1.
- This protocol not only reduces the communication overhead considrably, but also eliminates less informative messages which may impair the performance.
Experiments
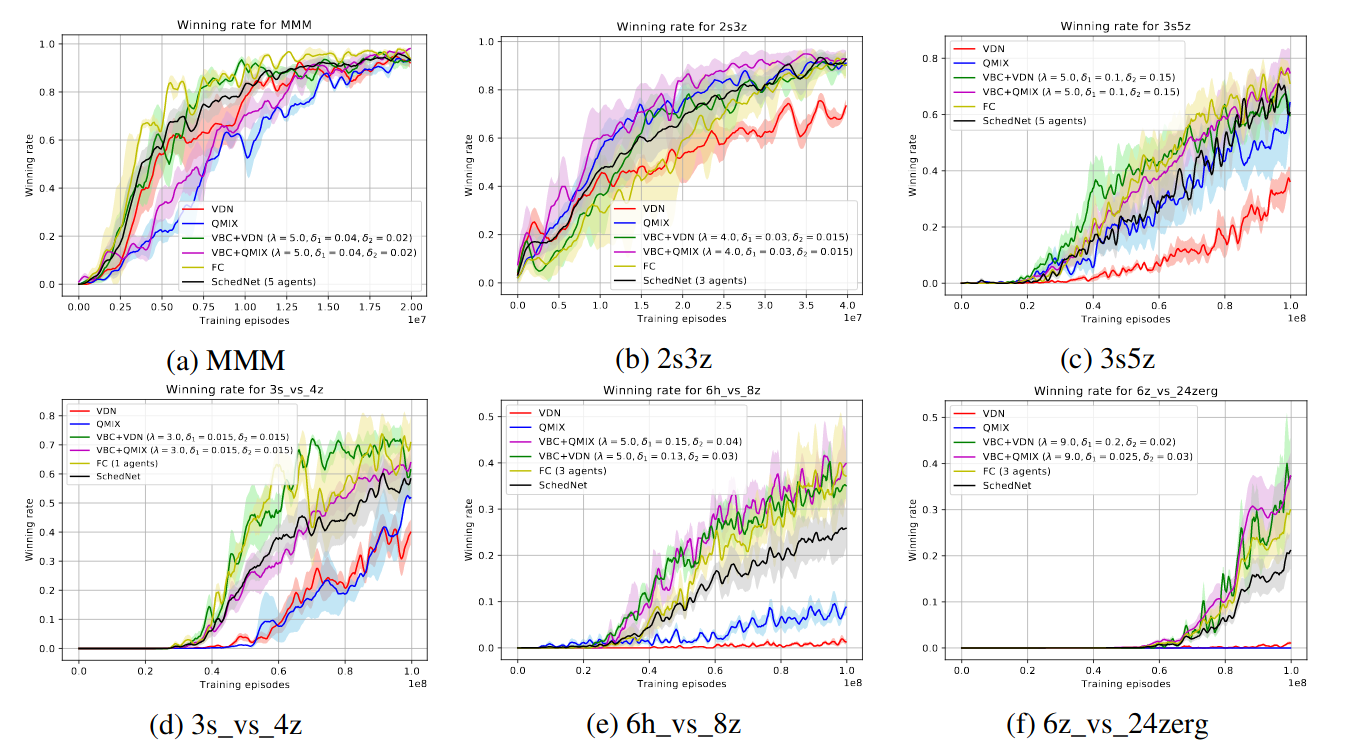
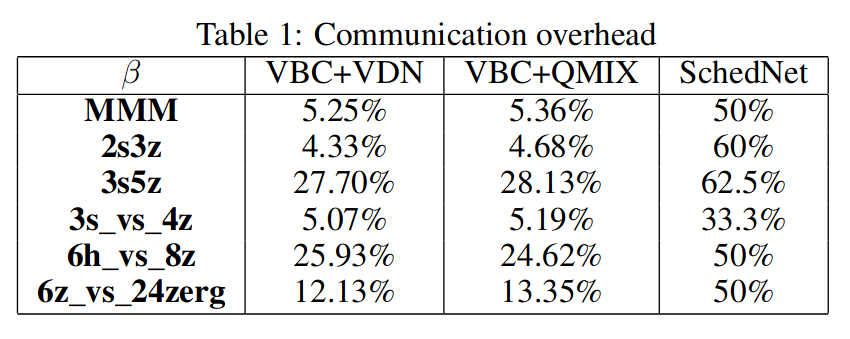
- VBC achieves a similar performance as FComm and even outplays FComnm for some tasks.
- This is because a fair amount of communication between the agents are noisy and redundant.
- By eliminating these undesired messages, VBC is able to achieve both communication efficiency and performance gain.
?
- SchedNet보다 Overhead에 있어서 좀 더 유연한 장점이 존재한다.
- 그치만 (IC3Net+) TarMAC 이랑 비교를 좀 해보면 좋을텐데.
- 간단한 Variance를 구하는 것(사실은 그냥 뺄셈)으로 좋은 시도를 한 것 같다. 물론 variance를 정확히 표현하지 못하긴 했지만 정보 자체의 quality나 impact를 이용한 논문으로 처음이지 않을까 싶다.
- 왜냐하면 다른 논문들은 그냥 connection을 네트워크가 알아서 찾도록 만들었는데, 얘네는 좀 더 구조화를 시도했다는 점이 존재하기 때문이다. 구조화를 시도했다는 부분은, 메세지 자체가 measure(dot product or L2 norm)를 계산하는데 이용되지 않았고, 메세지의 ‘효과(Q-value)’가 measure(variance)의 대상이 되었다는 점이다. ‘메세지는 그저 도울 뿐’이 아니라 더 멀리 떨어진 케이스인 듯 싶다. 어찌되었든 메세지의 정보에 대해서 직접적으로 파고든 내용은 아니었지만, 메세지의 효과에 대해서는 고민을 할 수 있는 논문인 것 같다.

Leave a comment